Comparison Of Autonomous System Routing Options Between Wide Area Networks
The choice of routing protocol is important in wide area networks. This article discusses some of the considerations involved in selecting an autonomous system (AS) routing protocol for a WAN.
Overview
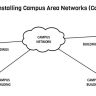
A wide area network (WAN) is a collection of computer networks that are geographically dispersed, but connected by a high-speed data link. This allows users in different locations to communicate with each other as if they were on the same local area network (LAN).
A wide area network (WAN) is a collection of computer networks that are geographically dispersed, but connected by a high-speed data link. This allows users in different locations to communicate with each other as if they were on the same local area network (LAN). The internet is an example of a WAN because it connects millions of computers around the world into one giant network.
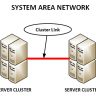
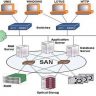
Routing Protocols
In this section, we will discuss the routing …