What Is A Wide Area Network?
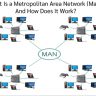
A wide area network (WAN) is the physical Internet. A WAN is a collection of different types of networks that are used to connect one location with another. The term “wide area” refers to the distance between the two locations and does not refer to how big or small either network may be.
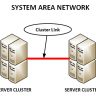
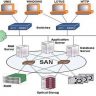
A WAN is the network of physical communications lines, fiber optic cables and satellite routes that connect multiple LANs in different locations.
A WAN is the network of physical communications lines, fiber optic cables and satellite routes that connect multiple LANs in different locations. A WAN can be used to connect LANs within a single building or campus, but it also connects sites that are located hundreds or thousands of miles apart.
The most common transmission media used by WANs include copper wire; fiber optic cable; microwave radio waves; satellite systems like Iridium Satellite or Globalstar Satellite; …