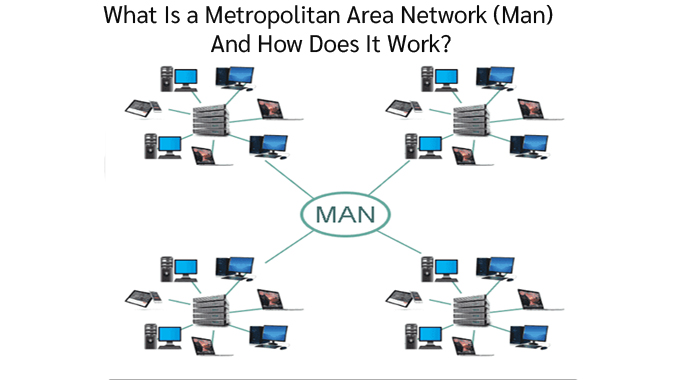
Understanding Wide Area Networks (WANs)
A wide area network (WAN) is a group of computers that are connected across a large geographical area. WANs allow data to be transmitted from one computer to another, even if the two computers are not in the same location or connected to the same network. WANs can connect multiple locations together, making it possible for people and businesses to work on projects and share resources with each other no matter where they are located.
What is a WAN?
A wide area network (WAN) is a private network that spans large geographic areas. WANs are used for communication between different locations, and they can be used to transmit data or voice communications.
A WAN allows you to connect with other networks that are not located in the same building or facility as your organization’s network. For example, if you have an office in New York City and another office in …