Why Every Technology Professional Should Study Network Topologies
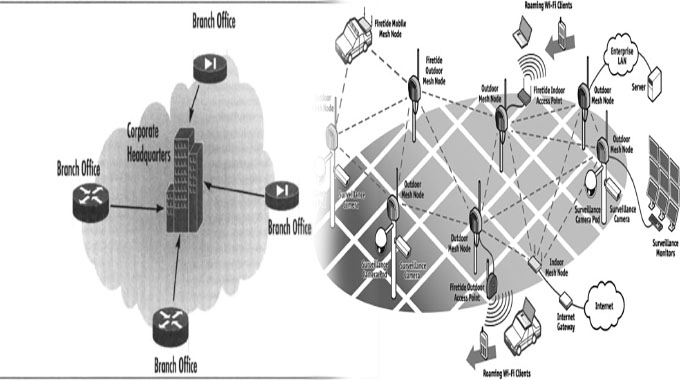
The network topology of a computer network is the layout or arrangement of its components. The term “topology” comes from geometry, where it means the study of shapes and spatial relationships between points, lines and surfaces. In computer networks, there are many different types of topologies based on how data travels through them. Different types of topologies also have different characteristics that make them better suited for certain situations than others
Topologies are a map of how connections are made between components in a network.
The term “topology” refers to the arrangement of nodes and links between them. It can be described as a map that shows how connections are made between components in a network.
The word “topology” comes from Greek, meaning “place” or “position”. A topology is thus an abstract representation of how things are placed relative to one another; for example, if you were building a house …