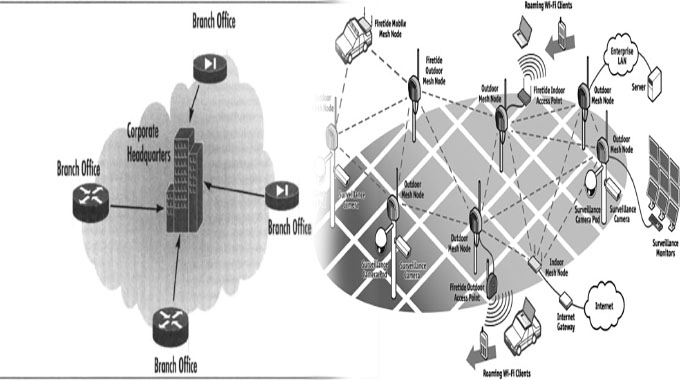
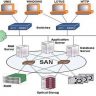
The Topology of an Enterprise Network
A topology is the physical arrangement of a network. In this article, we will discuss some common topologies and how they function.
A topology is the physical arrangement of a network.
A topology is the physical arrangement of a network. It determines how the network is connected and how data travels through it. Topologies can be divided into two main categories: linear and non-linear.
Linear topologies include bus, star, ring and mesh networks while non-linear topologies include tree and daisy chain (star).
Star topology
In a star topology, each node is connected to the central hub. All traffic must pass through the hub; therefore, if it fails or becomes disconnected from its power source, all other nodes will lose communication with one another.
The advantage of this type of network design is that it’s very easy to install and troubleshoot because all devices are located in close proximity to one …