The Internet is a wide area network (WAN), while your local area network (LAN) is a local area network. The difference between the two types of networks is that one covers a large area and the other covers a small area. Most businesses use both types of networks to expand their communications capabilities and improve efficiency.
A wide area network (WAN) is a communication network that covers a broad area.
A wide area network (WAN) is a communication network that covers a broad area. It can be used to connect geographically dispersed locations, such as branch offices of a company or campuses of an educational institution.
A WAN can be wired or wireless, but it must cover the entire area it serves, and it may include connections between different types of networks at each location (for example, Ethernet). An example of a WAN is the Internet: although most people think of the Internet as one large connected system, it actually consists of many smaller networks connected together by routers and other devices.
The Internet is a WAN, connecting your computer to millions of others.
The internet is a wide area network (WAN). It connects computers and other devices all around the world, allowing you to communicate with people from all over the world.
If you’ve ever bought something online or watched Netflix on your phone while traveling abroad, then you’ve used the Internet in action. The World Wide Web is one of many networks that comprise this WAN, which also includes private enterprise networks like those used by businesses or universities.
A local area network (LAN) connects computers in the same location.
A local area network (LAN) is a group of computers that are connected to each other. A LAN usually connects computers in the same location, such as in homes or small businesses.
LANs can be wired or wireless, but they’re most commonly wired because they’re faster and more reliable than wireless connections. When you plug your computer into a router with an Ethernet cable, it becomes part of your home network–and so do any other devices on the same electrical circuit as your router (iPhones, game consoles).
The difference between the two types of networks is that one covers a large area and the other covers a small area.
There are two types of networks: Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs).
A LAN is a network that covers a small area, such as your house or office building. It’s usually made up of computers that are all in the same location and connected with cables, wires or other devices like routers.
A WAN connects multiple locations across large distances, such as cities or states. It can also connect different countries together through the internet!
Most businesses use both types of networks to expand their communications capabilities and improve efficiency.
A LAN is a local area network that connects computers in the same location. A WAN, on the other hand, is a wide area network that connects computers that are geographically dispersed.
In practice, most businesses use both types of networks to expand their communications capabilities and improve efficiency. For example, if you have several offices located around the country or even around the world, you may want them all connected by one large network so everyone can share information quickly with each other regardless of where they’re located. This type of setup would be referred to as a wide-area network (WAN). If your business has just one office but still needs fast access between computers in different rooms or floors within that building’s walls, then it could benefit from setting up another type: an internal local area network (LAN).
A subnet mask in a router determines which nodes are allowed to communicate with each other.
A subnet mask in a router determines which nodes are allowed to communicate with each other. It’s a 32-bit binary number that looks something like this:
The first part of the subnet mask (0) tells us how many bits are reserved for identifying hosts or endpoints on the local network, and the second part (255) tells us how many bits are used for identifying other networks in our internetwork.
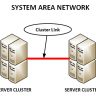
Routers are devices that connect multiple networks together over a single pathway or link, such as an Internet connection or cable modem line.
Routers are devices that connect multiple networks together over a single pathway or link, such as an Internet connection or cable modem line. Routers are used to connect LANs together. They can also be used to create larger networks by connecting routers together.
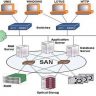
Routers can create virtual connections among LANs that are geographically dispersed by using different subnets for each LAN. This allows users on different LANs to see all other users on those same subnets as if they were all working from within their own local network environment.
Routers can create virtual connections among LANs that are geographically dispersed by using different subnets for each LAN. This allows users on different LANs to see all other users on those same subnets as if they were all working from within their own local network environment.
In order to do this, the routers need to be configured with routing protocols that determine which network should be used when there is more than one possible path between two hosts (or networks). Routers use subnet masks in determining which route should be used for a particular destination IP address; this process is known as “masking.”
WANs are a key part of any business’s communications infrastructure. They allow employees to connect remotely and work together as if they were all in the same office, which can improve efficiency and productivity. The Internet is one example of a wide area network that connects millions of computers around the world. LANs are local networks used by businesses or organizations within a single location such as an office building or campus–these types of networks are ideal for sharing files between coworkers without having to send them through email attachments every time someone needs access!