Comparison Of Autonomous System Routing Options Between Wide Area Networks
The choice of routing protocol is important in wide area networks. This article discusses some of the considerations involved in selecting an autonomous system (AS) routing protocol for a WAN.
Overview
A wide area network (WAN) is a collection of computer networks that are geographically dispersed, but connected by a high-speed data link. This allows users in different locations to communicate with each other as if they were on the same local area network (LAN).
A wide area network (WAN) is a collection of computer networks that are geographically dispersed, but connected by a high-speed data link. This allows users in different locations to communicate with each other as if they were on the same local area network (LAN). The internet is an example of a WAN because it connects millions of computers around the world into one giant network.
Routing Protocols
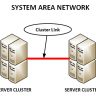
In this section, we will discuss the routing protocols that are used in WANs. Routing protocols are used to exchange information between routers in a network.
Routing protocols can be categorized into two main categories: distance vector and link state. Distance vector routing protocols send their entire routing table out to all of their neighbors every time they change it, while link state routing protocols only send partial information about their own links (i.e., those directly connected) when they change them
IGP vs. EGP
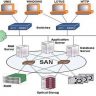
EGP is an exterior gateway protocol. It is used to exchange routing information between autonomous systems and other networks, like ISPs or private networks. It’s also used for routing information exchange between providers, but that’s not as common because it’s easier to use BGP instead of EGP when communicating with different providers.
IGPs
- IGPs are used to route traffic between routers within an autonomous system.
- A routing protocol that is used within an autonomous